What is Compressive Strength In Plastics?
Plastic compressive strength refers to the ability of plastic material to withstand compressive forces before it deforms or breaks. It is measured in stress units (such as pounds per square inch) and depends on the type and quality of the plastic.
That is contrary to tensile strength resisting loads leading to elongation. Compressive strength and tensile strength can be calculated separately. Compressive strength in plastics is all about materials being pushed together, and tensile strength is about materials being pulled apart.
ASTM D65 is the standard test for analyzing compressive strength in the United States. Some materials start to deform once the compressive strength yield point is exceeded (Some materials fracture at their limit). However, when a specific stress limit is exceeded, clasping occurs to prevent breakage, but that can cause a hurried and inconsistent change in the material’s compressive strength.
The clasping is peculiar to the compression test and is highly influenced by the material’s elastic modulus and the sample’s strain. Overstressing, which leads to fracturing of the sample, is called Ultimate compressive strength.
Compressive strength (MPa) is often analyzed on a Universal Testing Machine, and the measurement can also vary depending on the environment and specific testing methods.
The Testing Method
In mechanical testing, when a material sample is subjected to conditions that cause it to elongate or stretch out, the state is commonly referred to as being in tension. Conversely, when the sample experiences conditions that result in its contraction or shortening, it is characterized as undergoing compression.
These differing mechanical states involve contrasting physical forces but share underlying similarities at the atomic level. Speaking from an atomic perspective, atoms within the material are compelled to come closer together during the compression phase.
Atoms in a solid material constantly strive to achieve an optimal equilibrium position, seeking the right distance from their neighboring atoms to minimize internal energy. This process is subject to a balance of forces within the material that works against tension and compression.
In this context, the mechanisms at the atomic scale that govern both tension and compression states can be considered mainly analogous to each other. As previously noted, when a plastic material sample is subjected to compressive forces, it will typically experience a decrease in length, denoted by negative strain values.
In scenarios where the applied compressive forces exceed the material’s compressive strength, the sample may undergo structural changes beyond mere contraction.
Over-compression of the material could lead to problems such as clasping or buckling, which indicate the failure or compromise of the material’s structural integrity.
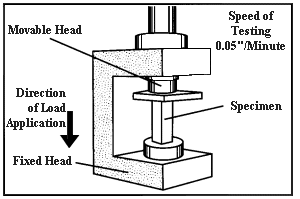
Mechanical Testing Apparatus: Analyzing Plastic Compressive Strength
The image illustrates a mechanical testing apparatus, specifically designed for tension or compression tests. The apparatus consists of a movable head and a fixed head. Between these heads, a specimen is clamped securely. When the test commences, the movable head applies force in the indicated direction, either stretching or compressing the specimen.
The testing speed is meticulously calibrated to 0.05″ per minute, ensuring consistent and controlled force application. The setup allows scientists and engineers to assess material properties, such as tensile strength or compressive resistance, by observing how the specimen reacts under the applied stress. It’s a fundamental tool in material science research and quality assurance.
Interesting Read – Physical Properties of Plastic Materials | The Complete Guide
Let’s see a table with compressive yield strength and compressive modulus of all the mainstream plastic materials.
| Materials | Compressive Yield Strength (MPa) |
Compressive Modulus (GPa)
|
| ABS | 65 | 2.5 |
| Acetal Copolymer | 85 | 2.2 |
| Acrylic | 95 | 3 |
| Nylon 6 | 55 | 2.3 |
| Polycarbonate | 70 | 2 |
| Polyethylene | 20 | 0.7 |
| HDPE | 20 | 0.7 |
| PET | 80 | 1 |
| Polypropylene | 40 | 1.5 |
| Polystyrene | 70 | 2.5 |
Difference Between Compressive Strength and Compressive Modulus
The basic difference between them can be attributed to the compression yield strength, a unit for measuring a material’s stress. On the other hand, compressive modulus represents both stress and strain.
Compressive strength measures the maximum stress a material can withstand under compressive loading before it fails or fractures. It is typically reported as a stress value (such as pounds per square inch or megapascals) and is determined through experimental testing. Compressive strength is essential for polymers subjected to high compressive loads, such as in construction and engineering applications.
On the contrary, Compressive modulus denotes the stiffness of a plastic material when subjected to compressive loading. It corresponds to the gradient of the stress-strain curve within the linear elastic range and is commonly expressed in stress units divided by strain (for instance, pounds per square inch per inch or megapascals per percent). Compressive modulus is particularly relevant for materials that undergo compressive loads without breaking down.
Engaging Read – Mechanical Properties of Plastic Materials | The Definitive Guide
FAQs
Below are the frequently asked questions on HDPE compressive strength and compressive strength of plastic. Let’s dig deep to know more.
What is the difference between flexural strength and bending strength?
The type of material being tested usually classifies the difference. A flexure test is conducted to test the bending strength of brittle material. On the other hand, a bend test is designed to measure the crack resistance of a pliable material.
How do you calculate bending strength?
We have to do some math – Let’s take F as a force applied, L as the length of the sample, W as the width of the sample, and D as the depth of the sample. To get the bending strength, multiply the force by the length of the sample and then multiply it by 3.
What is Modulus Strength?
Modulus strength means a force of a specific elongation value. It is expressed by units MPa and psi.
What is the difference between flexural strength and compressive strength?
Tensile strength means the ability of materials to withstand bending, and flexural strength is the ability to resist rupture. The simplest way to find a material’s flexural strength is by raising its compressive strength to 2/3 power and multiplying it by 2.3.
How crucial is Young’s Modulus?
Young’s Modulus is one of the most important factors when using a material for any application. It can determine the behavior of a material when subjected to force. Whatever we see around us, such as buildings, flyovers, roads, and other structures, are built around the same concept of force.
Suggested Read
- Thermal Properties of Plastics | The Ultimate Guide
- HDPE Melting Point | HDPE Repeat Unit | HDPE Properties | HDPE Advantages & Disadvantages
- ABS Melting Point, Properties, Applications, Advantages & Disadvantages
- PLA Melting Point, Properties, Applications, And Advantages & Disadvantages
- What is Biodegradable Plastic? | Types of Biodegradable Plastics | Biodegradable Vs. Compostable | Properties | Applications of Biodegradable Products
- What is Bakelite?: The Plastic That Changed the World
Final Thoughts
To sum up, the compressive strength of plastic is a critical property for evaluating its capacity to endure compressive forces. It is crucial to consider in applications involving such loads, including construction, engineering, and packaging.
The compressive strength of a plastic material is determined by various aspects, such as its molecular structure, additives, and processing conditions.
Selecting the appropriate plastic with adequate compressive strength is essential for ensuring the safety and longevity of the end product.
With continuous research and development in the plastic materials industry, the compressive strength of plastics is being enhanced, creating new opportunities for a diverse range of applications.
Kindly share your reviews and thoughts in the comment box.
Have a wonderful day.
Quick Navigation