Greetings, esteemed readers, I trust you’re in good health. Today, I am poised to present a comprehensive and visually engaging guide on TPU material. I invite you to prepare for an enlightening journey and delve further into the reading.
What is TPU?
TPU or Thermoplastic Polyurethane, represents a class of plastics synthesized through a polyaddition reaction involving a diisocyanate and one or more diols. Its versatile nature allows it to function as a soft engineering plastic or an alternative to rigid rubber materials.

TPU rubber or plastic (yes, you can call it both) provides extraordinary benefits because of its thermoplastic nature – excellent load-bearing capacity, high elongation at break, and tremendous tensile strength.
The blended material can be utilized as soft engineering plastic and soft rubber—the different ranges of inbuilt hardness(Shore 30A – Shore100A).
TPU material is also a premium additive for other thermoplastics like Polycarbonate and ABS to improve their tensile strength.
A TPU and ABS or PC composite will have a flexural modulus of up to 150000 psi. However, TPU has a tensile strength of around 5076 psi (for Shore 70A).
How is TPU Plastic Made?
The three basic processes for making TPU are:
- Chemical Synthesis
- Prepolymer Formation
- Chain Extension
Chemical Synthesis
The fundamental process begins with chemical synthesis. TPU is synthesized by polymerizing a diisocyanate with a polyol and a chain extender.
The common diisocyanates are MDI (Methylene diphenyl diisocyanate) or TDI (Toluene diisocyanate), while polyols are typically polyester or polyether types. The chain extenders are often short-chain diols.
Prepolymer Formation
Initially, the diisocyanate and polyol are reacted to form a “prepolymer.” This step is usually performed in a high-temperature, controlled environment to ensure full reaction.
Chain Extension
The prepolymer is then reacted with the chain extender. This extends the molecular chain and forms the thermoplastic polyurethane polymer.
Typically, the reaction occurs in the presence of a catalyst to accelerate the process.
It is a specific segmented block polymer comprising soft and hard segments.
Hard Segment: It comprises a chain extruder and an isocyanate making TPU tough and rigid and producing its physical performance properties.
Soft Segment: It is constructed from a polyol and an isocyanate and gives TPU material flexibility and elastomeric characteristics.
Engaging Read – What is TPV Material? | A Simple and Detailed Guide
Main Properties of TPU Rubber/Plastic
Here I will try to explain the properties in detail. Let’s begin:
- Optimum Comfort
- Scratch Resistance
- UV Resistance
- High Transparency with Abrasion Resistance
- Compatibility with ergonomic Applications
Optimum Comfort
TPU filament provides optimum comfort for customers using sportswear, footwear, buildings, and construction materials. It is believed to be highly breathable. If the customers prefer comfort over cost, TPU is ideal.
Multiple grades should be utilized depending on the comfort range and quality.
Grades with values as high as 10,000 g./m2/day (+560%) are considered the best. Typical TPU has a vapor transmission below 1 500 g./m2/day.
Traditional TPU material can be modified with breathable ones to tune the breathability according to the needs.
Scratch Resistance
When the priority is scratch/abrasion resistance, thermoplastic polyurethane must be preferred over any thermoplastic materials.
Thanks to that ability, TPU plastic has become integral to automotive, industrial applications, sports, leisure, and wires and cables.
The scratch resistance of a material is determined by measuring the weight loss of a product in a standardized wear test, and TPU ranks way above all the mainstream thermoplastics, making it the best.
UV Resistance
Aliphatic TPU maintains good color stability for your aesthetic parts.
They exhibit tremendous resistance to UV radiation and great color stability while not compromising necessary mechanical properties.
The aliphatic TPU’s characteristics and compliance make it perfect for electronic applications. Organizations can bank their scratch and UV resistance properties for all colored products.
High Transparency with Abrasion Resistance
Clear and translucent TPU with good hardness is readily available in the market. That makes it applicable in producing transparent films and tubes through extrusion or even in injection molding technical aesthetic or glossy parts where transparency and thickness of up to 6mm can be attained.
| Property | Temperature | Value |
| General | ||
| Density | 23.0 °C | 1.05 – 1.34 g/cm³ |
| Mechanical | ||
| Tensile Strength | 23.0 °C | 20 – 60 MPa(at 350-800% strain) |
| Elastic modulus | 23.0 °C | 0.03 – 0.7 GPa |
| Elongation | 23.0 °C | 350 – 800 % |
| Thermal | ||
| Specific heat capacity | 23.0 °C | 1500 – 1700 J/(kg·K) |
| Thermal conductivity | 23.0 °C | 0.14 – 0.5 W/(m·K) |
| Flammability | UL 94 HB | NA |
| Melting point | NA | 120 – 220 °C |
| Max. service temprature – long | NA | 80 – 90 °C |
| Max. service temprature – short | NA | 120 – 135 °C |
| Coefficient of thermal expansion | 23.0 °C | 1.1E-4 – 1.7E-4 1/K |
| Electrical | ||
| Electrical resistivity | 23.0 °C | 1.00E+9 – 1.00E+12 Ω·m |
| Dielectric constant | 23.0 °C | 4 – 7 [-] |
| Technological | ||
| Transparency | NA | Yes |
| Application Areas | – | Cable sheathing, winter sports equipment, ear tags, mobile cases, etc. |
| Processing Methods | – | Injection molding, blow molding, extrusion. |
Other Key Advantages
- Across all ranges of hardness, elasticity is always maintained. Various additives can improve heat resistance, dimensional stability, and fungus resistance, reducing friction and weatherability.
- Additives like UV absorbers, anti-oxidants, and anime stabilizers protect polyurethanes from UV-light oxidation. Thus TPU material becomes compatible with applications demanding light or thermal stability.
- Aromatic TPUs are another functional variation strong enough to withstand microbes and chemicals. A considerable drawback is wearing attractiveness caused by prolonged exposure to heat and UV light. However, the degradation doesn’t leave any long-lasting impact but can cause discoloration and (in the worst case) loss of physical properties.
- On the other hand, allopathic TPU filament is naturally light and stable and can easily withstand discoloration or any further damage from UV exposure. That makes them suitable as laminates overlap on glass and glaze.
Limitations of TPU
- Drying time is necessary before processing.
- A bit more expensive compared to other alternatives.
- The confined temperature range for the processing doesn’t help make the process any faster.
- Some grades have a relatively short life cycle, which can add costs.
- Requires special manufacturing conditions across all the significant methods.
Related Read – What is TPR Material? | The Definitive Guide
Thermoplastic Polyurethane Processing Methods
TPU is a melt-processable material compatible with traditional processing methods like Injection molding, extrusion, compression, and blow molding. TPU can be easily fabricated into many shapes and sizes to create various products.
TPU filaments are often combined with organic solvents to form laminated textiles and functional additives.
For the smoothness of the process, drying is compulsory. Removing the moisture before processing is essential, or it will lead to loss of physical properties and brittleness.
Largest TPU Suppliers in the World
| Company | Brand(s) | Based in: |
| Covestro | Desmopan® | Germany |
| BASF | Elastollan® | Germany |
| Huntsman | IROGRAN®, KRYSTALFLEX®, AVALON® | United States |
| PolyOne | NEUSoft™, OnFlex™, Edgetek™, Gravi-Tech™, | United States |
| DowDuPont | DIPRANE™, HYPERLAST™ | United States |
| Lubrizol | Pearlbond™, Isoplast®, Pearlstick™, Estane® | United States |
| Epaflex | EPAMOULD, EPACOL TK, EPALINE | Italy |
Types of TPU Films
Three main types of TPU film are available in the market – Polyester, Polyether, and Polycaprolactone.
| Polyester | Polyether | Polycaprolactone |
| Constructed by ester subunits joining with each other by a method called ring-opening polymerization | Made by ether subunits combining in a process called ring-opening polymerization | Similarly, Produced by caprolactone subunits linking with each other by ring-opening polymerization. |
| Compatible with PVC and other polar plastics | Slightly lower in terms of gravity than serval grades of polyester & polycarbonate | Exhibits inherent toughness and resistance to polyester-based TPUs |
| Fabulous abrasion resistance | Fantastic hydrolysis resistance | largely unaffected by oils and chemicals |
| Resisnt to oils and solvensts | Low-temperature flexibility | Low resistivity to high temperature and hydrolysis |
| Excellent balance of physical properties | Can easily microbial attack | A high degree of crystallinity |
Applications of TPU Filaments
TPU’s easy processability and versatility make it ideal for several applications. Let’s discuss the leading applications.
- Mobile Cases
- Automotive
- Textile Coatings
- TPU sheets
- Seals and Gaskets
- Sports and Leisure
- Tubes and Hoses
- Belts & Profiles Industry
TPU Cases
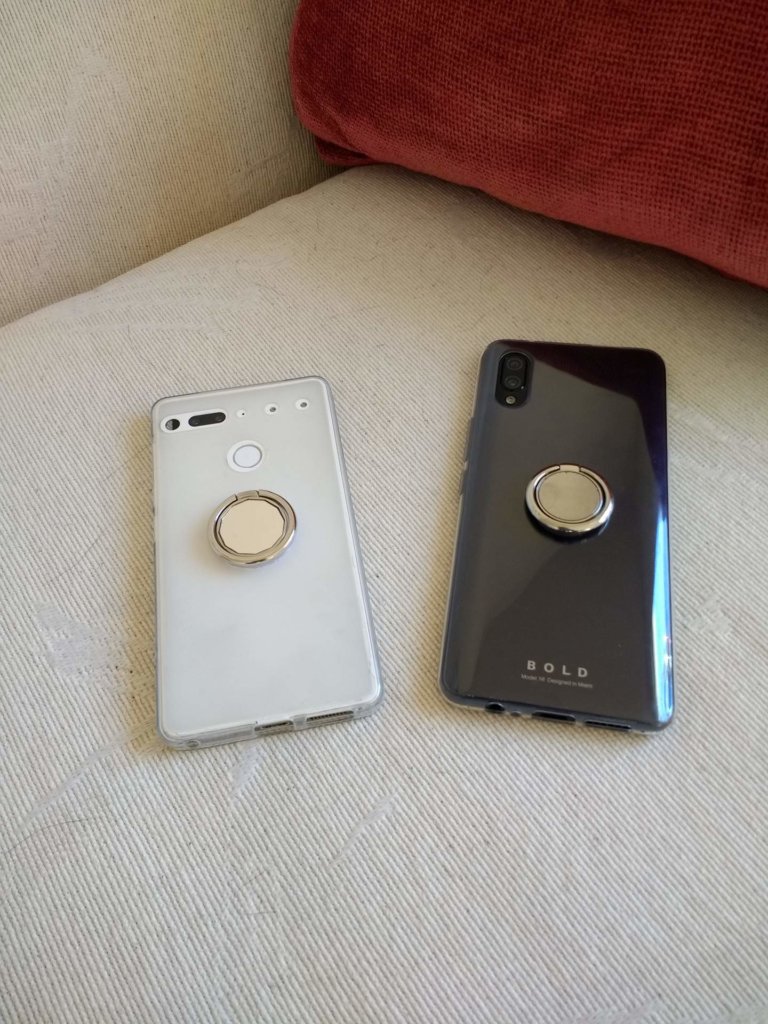

Perhaps the most popular TPU-made product among the masses is phone cases. Cases made from thermoplastic polyurethane are flexible, stylish, and, most importantly, long-lasting (if you don’t want to keep buying new cases).
The only drawback is that the cases will be more susceptible to everyday wear and tear. However, the case will still provide reasonable protection for your phone.
Automotive
TPU boasts fantastic scratch and aging properties, making it an excellent choice for the highly sophisticated automotive industry. Thanks to its fast molding cycles, it’s a cheaper solution for manufacturers.
Aging and scratch resistance properties and its inexpensive nature make TPU material applicable in gear knobs and console parts.
Textile Coatings
Sintering, calendering, or T-die lamination processes should be utilized for textile applications. TPU plastic’s terrific mechanical properties, chemical resistance, and weldability make it suitable for coating applications like inflatable items, converter belts, military equipment, etc.
TPU Sheets
TPU sheets provide unmatchable performance and quality for specific products. Among the most common applications for TPU fils are textile coatings, inflatables, garments, adhesives, and barrier films.
T-die, calendering, and blown-extrusion film processes are advisable for laminated films and sheets.
Seals & Gaskets
Seals and gaskets help in preventing leaking of some sort. Particular TPU filaments and additives have recently been developed to meet the rapidly growing demand for thermoplastic with adequate oil resistance and a meager compression set.
Industrial high-pressure hydraulic seals are prime examples of such modification, as they significantly improve their flow properties and lower compression ratios.
Sports and Leisure

Various sports and leisure items, like jackets, shoes, etc., are made from TPU to take advantage of its supreme flexibility, clarity, good paintability, and environmental resistance.
Tubes & Hoses
Hoses and tubes are essential for the smooth handling of objects. The tremendous durability for working correctly. That’s where TPU comes in with durability and flexibility not easily found in other thermoplastics; not just that mechanical, chemical, and kink resistance makes it irreplaceable.
Prime applications include hydraulic wire bond hoses and pneumatic tubing.
Belts & Profile
TPU materials are well-known in the belts and profile industry for producing premium products. For example – converter belts, timing belts, etc.
TPU’s Creep resistance and long-discussed mechanical strength are to be noted here.
The Future of Thermoplastic Polyurethane
According to research conducted by marketsandmarkets, TPU will register a CAGR of 7.1% till 2024 to gross sales worth USD 3.5 Billion. The largest industry in terms of TPU consumption is footwear, and according to us, it will remain at the top for quite some time.
Other segments like automotive, medical, electronics, and industrial machinery are growing rapidly for TPU.
Asia-Pacific remained the largest consumer of TPU plastic in 2020. It will remain the leader, growing its market share till 2024, followed by Europe, North America, the Middle East & Africa, and South America.
TPU Market Share by region
Source – marketandmarket analysis
Of all the TPU films, polycaprolactone is the most used and fastest-growing market.
Things can be hindered due to the ongoing Covid-19 pandemic. Still, looking at the world tussle to win over history’s most severe pandemic, the vaccine’s rollout can make things bright and sunny once again for the world’s economy and manufacturing industry.
FAQs

Is TPU material BPA free?
TPU does not contain Bisphenol-F (BPF), Bisphenol-S (BPS) or Bisphenol-A (BPA), or any other similar compounds (unlike polycarbonate or other epoxies) as it doesn’t require any of these to process.
Is TPU better than PVC?
Both materials have pros and cons, but TPU tends to be tougher than PVC. Polyvinyl chloride has low shear strength. TPU is also sturdier because it has a high abrasion resistance that will withstand scratching and scuffing. Another point in TPU’s favour is that it is more environmentally friendly.
Why do TPU cases turn yellow?
A TPU case will turn yellow when sunlight, heat, or certain chemicals are exposed. The colour change is caused by natural degradation and is irreversible. The yellowish colour won’t vanish with cleaning or bleaching. Although the yellowing is very normal, it doesn’t affect the case’s durability.
Does TPU need cooling while 3D printing?
Usually, TPU doesn’t need a cooling fan, but a lot depends on your settings. For example, 3D printing with TPU without a cooling fan is normal, but a cooling fan at around 40% is recommended if printing at high temperatures and speeds. Using a cooling fan is also important when you have bridges.
How fast can you 3D print with TPU?
The flexible TPU filament print speed should be 30 to 50 mm/sec. The optimum setting for the layer thickness is 0.1mm. Extrusion temperature ranges from 200 to 220˚C with a heated bed platform around 80 to 100˚C.
What is the difference between TPU and PLA?
TPU and PLA have some subtle differences. PLA is more environmentally friendly and compostable. It is easier to print and can prove to e an ideal material for beginners. TPU is suitable for molding flexible parts that need to be able to return to their original state.
Suggested Read
- What is PVDF (Polyvinylidene Fluoride) | A Detailed Guide
- What is UHMW Plastic Material? | The Definitive Guide
- What is PTFE (Polytetrafluoroethylene)? | The Complete Guide
- What is HDPE Material? | HDPE Properties | Advantages of HDPE | Disadvantages of HDPE | The Future of HDPE
- What is LDPE? | Low-Density Polyethylene | The Complete Guide
- What is Polyethylene? | How is Polyethylene Made | Types of Polyethylene | Processing of PE
The Takeaway
To conclude, thermoplastic polyurethane (TPU) has emerged as a multifaceted and innovative material, effecting transformative changes across various industries, thanks to its distinctive properties.
Its elasticity, coupled with its robust resistance to oil, grease, and abrasion, not to mention its versatility across a broad spectrum of temperatures, earmark it for an array of applications spanning from medical equipment to sportswear.
As advancements in research and technology continue, the scope for TPUs is set to broaden, further cementing its position as a material of the future.
Kindly share your thoughts and reviews in the comment section.
Have a Fantastic Day.
Quick Navigation

Sagar, thanks. A good elaboration on TPU. .
Some kitchenware companies, e.g. Zwilling, make chop board from TPU.
Is it safe for health just in case some TPU debris going into human body?
I don’t think any plastic material going into the human body is safe, however, I think the companies, especially big companies must be taking the necessary precautions while making their products.
I’m looking for someone to speak to the “grippability” of mobile phone cases made from TPU. You mention flexibility, which is more than the largest online seller is willing to say on its website as well as in response to my query. It’s all about protection, never prevention, and while I want protection, I’d just as soon my phone didn’t slip out of my hand in the first place. Would you address this issue please?
Why are there more TPU fabric manufacturers in the USA? is it due to EPA restrictions?
“Are there any TPU fabric manufacturers in the USA?
Highland Plastics is the only name in my mind.
Hi There, are there sustainability aspects to TPU? I’m looking at creating some pet products using it. Thank you!