Not Allpalstics can be used for food applications, some are safe, and some are not. I’m here with a detailed piece on the best food safe plastics that are safe for you and your family.
Food Grade Plastic: The Explanation
A food grade plastic is a plastic material that is food safe and is approved by Food and Drug Administration (FDA) for contact with edibles. They are called food contact substances (FCS). For creating quality food packaging, it’s crucial to understand which plastics are food safe as some acidic foods or liquids can leach chemicals from the packaging.
The FDA describes food contact substances as “any substance that is intended for use as a component of materials used in manufacturing, packing, packaging, transporting, or holding food without the risk of technical effects affecting the food.”
The “technical effects” expound leaching, affecting the taste of the food & beverages and posing a risk to human life when affected material is consumed.
How to Identify Food Grade Plastics
Figuring out whether a plastic material is food grade or not is very easy. The best way to check is to look for the Resin Identification Code—i.e., recycling number. It helps in identifying the type of plastic material. The code is any number between 1 to 7 stamped between a triangle made by arrows. Typically, “1” and “7” indicate food grade plastics.
Without further ado, let’s begin with or list of the best food grade plastic materials:
- Polyethylene Terephthalate (PET or PETE)
- Polypropylene (PP)
- High-Density Polyethylene (HDPE)
- Low-Density Polyethylene (LDPE)
- Polycarbonate (PC)
1. Polyethylene Terephthalate (PET or PETE)
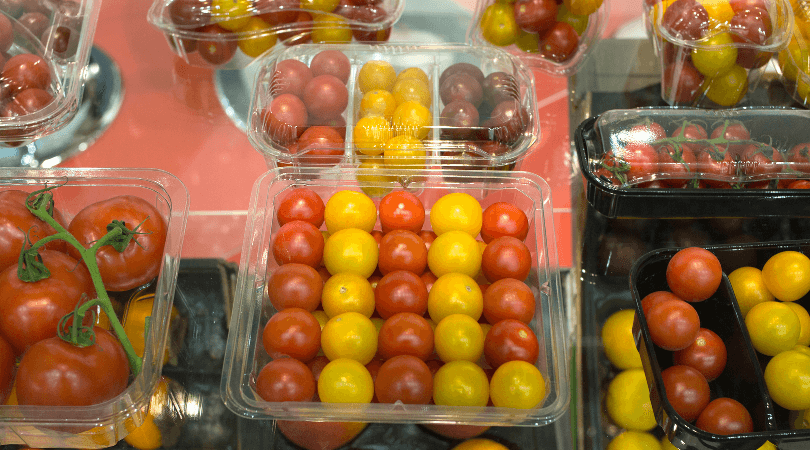
PET goes by the FDA code “1” and is the most utilized thermoplastic globally, with a wide array of applications found in electronics & electrical, packaging, automobiles, films, and textiles. The industry most uses PET is the textile industry, and the second-largest utilizer is the food packaging industry.
Polyethylene Terephthalate has a semi-crystalline structure and looks colorless. In addition, it exhibits high strength and flexural modulus, supreme wear resistance, excellent dimensional stability (impressive strength to weight ratio), good water resistance, and impact strength.
The excellent physical properties and chemical imperativeness make PET an ideal material for food applications. Common examples are bottles and containers for mineral water, alcohol, carbonated drinks, transparent films, sheets, packaging trays, blisters, etc.
Engaging Read – Plastic Thermoforming Mold: Information about Male Vs. Female Molds
2. Polypropylene (PP)
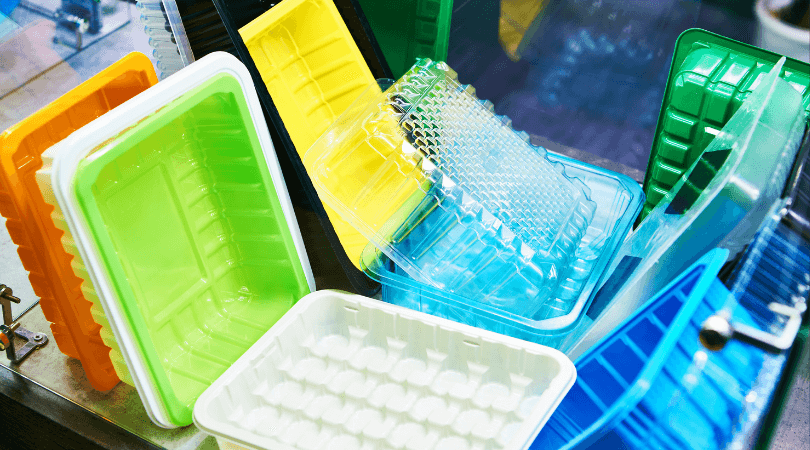

Polypropylene goes by the FDA code “5”. It is a crystalline thermoplastic made from a blend of different propylene monomers. It has a high melting point and demonstrates outstanding thermal resistance, making it an ideal choice for dishwashers or microwaves.
It is also known for its toughness and rigidness, and being resistant to many external factors makes it a manufacturer-friendly plastic material. In addition, properties like water resistance, good fatigue resistance, withstanding ability to biological conditions like algae, fungi, and bacteria, high electrical resistance, cost-effectiveness, and recyclability make it a brilliant choice as a food-grade plastic.
It is preferred to make packaging trays and blisters for storing vegetables, meats, and fruits in the food packaging industry.
3. High-Density Polyethylene (HDPE)
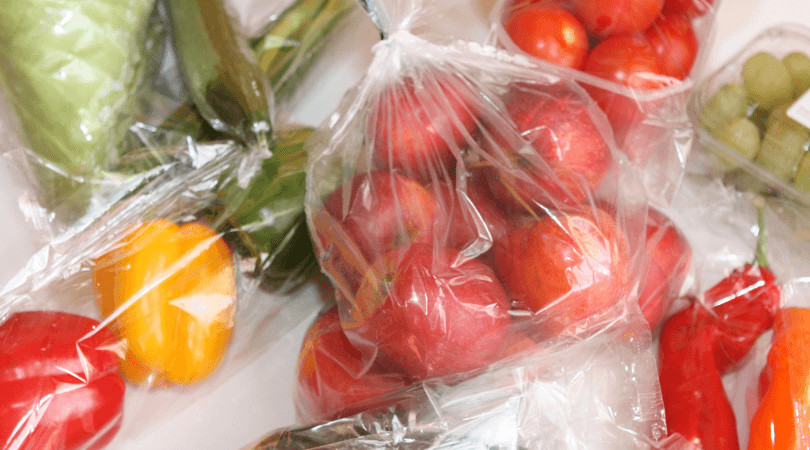
HDPE or High-Density Polyethylene has FDA code “2” and is a tough and rigid thermoplastic material known for its outstanding tensile strength, low cost, high melting point, and good impact strength. It is resistant to corrosion, cracking, and weathering and exhibits good withstanding ability towards mold, insects, rot, and mildew.
The food safe plastic has a tremendous strength-to-density ratio of 0.93 to 0.97 g. When seen under a microscope, it is noticeable that HDPE has a linear structure with little branching, resulting in a stronger molecular structure and greater tensile strength.
The common applications include food grade plastic containers, squeeze bottles (e.g., butter, chocolate syrup, vinegar, etc.), grocery bags, liquid food jugs, etc.
Engaging Read – What is the Glass Transition Temperature of Plastics?
4. Low-Density Polyethylene (LDPE)
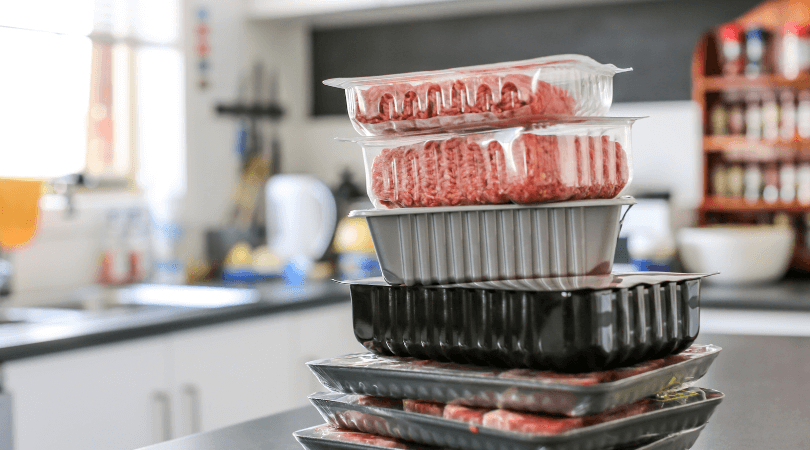

Like HDPE, LDPE also belongs to the polyethylene family of thermoplastics. It is lightweight, tough, soft, and flexible in nature. It is well-known for having excellent corrosion resistance, good impact resistance, good chemical properties, and low-temperature compatibility.
LDPE is more branched out in its structure than in perfect rows, making it low in density; thus, it is often considered ideal for applications where structural strength and stiffness are prioritized.
LDPE’s other valuable properties are fantastic electrical insulating properties, great resistance to alcohols, and acids, dilute alkalis, high impact at low temperature, cost-effectiveness, and good processability. The most common food-grade plastic packaging applications are bread bags, six-pack rings, produce bags, and can lids.
5. Polycarbonate (PC)
Polycarbonate has an FDA code “6,” which is FDA approved for food applications. Still, there has been an ongoing concern about the health effects of bisphenol A (BPA) – The main component used to manufacture polycarbonate. However, according to a recent analysis of the FDA on PC, it has a very low level of BPA and is safe for food applications.
Polycarbonate is amorphous, rigid, and transparent thermoplastic material is known for its high impact strength (200 times stronger than glass), high dimensional stability, and good electrical insulating properties; and is also transparent with internal reflection, and transmission capacity is as good as glass making it a good choice for not just food packaging applications, but also heavy dusty industrial applications.
It shows good chemical resistance to chemicals like aliphatic hydrocarbons, dilute acids, and alcohols. Modest resistance towards oils and greases. It’s affected by aromatic and halogenated hydrocarbons and diluted alkalis.
It is ideal for making strong, rigid water and beverage bottles and large amounts of food products.
Fascinating Read – 7 Types of Plastics | An Helpful Illustrated Guide
FAQs
1. What is the best food grade plastic?
Ans. HDPE is called the best food safe plastic. It is given the FDA symbol “2”. HDPE is one of the most stable and most inert forms of plastic with features like corrosion resistance and less moisture absorbent, making it the best choice for any food-storing application.
2. Which plastics should never be used for food applications?
Ans. Although upto some extent, used in food applications, polystyrene should be avoided as it is suspected to contain carcinogens. It comes with FDA grade “7” and uses several food packaging applications like coffee and tea cups, plastic cutlery, takeaway containers, and trays.
3. Is food grade plastic safe to microwave?
Ans. According to the world health organization (WHO), microwaving food is generally safe. However, microwaving in plastic containers is linked to increased leaching. Importantly, even if a plastic container is labeled “microwave safe,” it simply means it won’t melt inside a microwave.
4. Is it necessary to use food safe plastics?
Ans. Using FDA-approved food grade plastic is extremely important because food grade plastics won’t adversely affect your health. Whether you are preparing food and beverages for the masses or in your home, using food grade plastic containers will help ensure your family’s health.
5. Can recycled plastics be used for making food containers?
Ans. Recycled plastics are defiantly utilized for making food containers and plastic bottles as well. Because of focused recycling programs across the world, more than 300 million PET bottles are made from recycled plastics.
Suggested Read
- What is Liquid Plastic? | Liquid Plastic Vs. Resin | An In-Depth Guide
- Antistatic vs. Static Dissipative Plastics | Which One to Choose?
- LDPE Vs HDPE: What are the Differences and Similarities
- What is PVDF (Polyvinylidene Fluoride) | A Detailed Guide
- What is Injection Molding Wastage? | Remedies to Reduce Plastic Waste
- What is the Best Glue for Plastic Parts | The Ultimate Guide
- What is Thermoforming | Different Stages of Thermoforming | Types of Thermoforming | Applications | Advantages & Disadvantages
- Plastic Abbreviations and Their Salient Features | The Ultimate Guide
The Conclusion
That was all I wanted to say about food grade and food-safe plastics. Using products made from FDA-approved plastics and spreading awareness about it is extremely important for the well-being of not just your family but also society.
I hope you enjoyed the article. Kindly share your thoughts and feedback in the comment box.
Have a Fantastic Day.
Quick Navigation


Is there any literature on xenoestrogens in food grade plastic?
NCBI has valuable information on food grade plastics and xenoestrogens present in it.
Nylon SGF15 Natural is a Food Grade or Not ? Please confirm…..
It is a food grade-plastic