What is TPE Material?
TPE Material (Thermoplastics Elastomers) is also known as thermoplastic rubbers. It belongs to the family of thermoplastic rubber materials with TPR, TPU, and TPV. It has most characteristics similar to thermoplastics and thus is used in several applications. TPE is also considered a successful blend between plastics and rubber like other thermoplastic rubbers.
When heated, TPE becomes free-flowing, and that flowing tendency increases when sheer force is applied. When cooled down, it regains its original shape and structure(A prime characteristic of traditional thermoplastics).
TPE material goes through physical cross-linking, which the additional heat application can alter.
That feature and its elastomeric component make recycling and reusing the production waste easy.
Thermoplastic elastomers are soft in nature, making molding or extruding other thermoplastic materials easy.
It is also quite popular in applications like healthcare, automotive, wires & cables, footwear, electronics, etc.
The popular grades of TPE material are supplied by teknor apex. They are produced and supplied under 6 different trade names representing various applications and technologies – di- and tri-block hydrogenated styrene block copolymers (Tekron, Elexar, and Monprene), thermoplastic vulcanizates (Uniprene), thermoplastic polyolefin blends (Telcar), Tekbond are a few of them.
TPE Plastic: Key Properties

The shore scale can measure the softness of the material. The usual softness comes at 20 Shore OO up to 90 Shore A.
Manufacturers highly prefer TPE material due to significant cost savings and its easy processability.
Any conventional rubber is a thermosetting material, which must undergo a chemical cross-linking reaction during molding, usually called vulcanization.
The reaction makes it possible to be processed in traditional thermoplastic machinery.
The vulcanization reaction takes around 1 minute to several hours to complete(though various factors are responsible for infusing the time).
On the other hand, thermoplastic molding for TPEs omits the cross-linking process and makes the cycle times much faster, which can be as little as 30 seconds.
- TPE products are recyclable, and the production waste and scarp can be re-processed. At the same time, most thermosetting elastomers end up in landfill.
- Fantastic resistance to most chemicals(oils, alcohols, greases, aromatic and aliphatic hydrocarbons, dilute alkalis) and weathering.
- Excellent flexural fatigue resistance
- Good colorability
- Low specific gravity
- Decent electrical properties
- Great wear and tear resistance
Advantages
- TPE plastic is an engineering marvel, combining the looks and flexibility of thermosetting rubber with the processing prowess of plastics.
- It has high elasticity and encompasses various compression sets, durometers, and excellent elongation.
- The excellent processability makes it compatible with bulk manufacturing with injection molding or extrusion. The reclaiming and recycling benefit is the cherry on top of the cake.
- Thermoplastic elastomer products have excellent thermal properties and stability when exposed to a broad range of environmental effects.
- Reduction in detrimental pollution is another crucial benefit over traditional thermoplastics as TPEs consume less energy during production and can be easily recycled.
- TPE polymer is an inexpensive alternative to silicone, latex, and PVC compounds – It can be used for tuning applications mostly influenced by thermoplastics
- It can be colored easily with most dyes.
- It has improved consistency in terms of both raw materials and finished products. The materials require no-reinforcing agents, little or no compounding, and cure systems, making them super-efficient without any dissimilarities within batches.
Disadvantages
- Drying might be required before processing.
- The number of low-hardness products manufactured by TPE is quite low
- Softens at high temperatures
What Are The Most Popular TPE Material Grades?
- Thermoplastic Polyolefins (TPE-O or TPO)
- Styrenic Block Copolymers (TPE-S)
- Thermoplastic polyurethanes
- Melt processable rubber (MPR)
- Thermoplastic polyether block amides
Thermoplastic Polyolefins (TPE-O or TPO)
This TPE polymer variation is a blend of polypropylene and uncrosslinked EPDM rubber. A low degree of crosslinking is deliberately made in exceptional cases to improve heat resistance and compression set properties.
The blend is mostly used in applications with high toughness, such as automotive bumpers and dashboards.
The properties align with the high hardness scale ->80 Shore A and meager elastomeric properties.
Styrenic Block Copolymers (TPE-S)
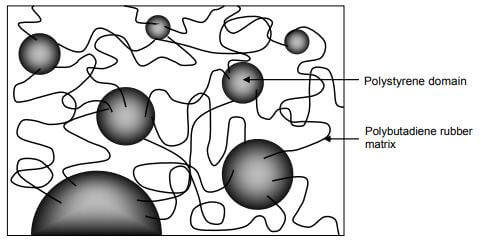
Source: Thermoplastic Elastomers, Edited by Prof. Adel El-Sonbati
The TPE-S polymer consists of two-phase block copolymers with hard and soft fragments – Styrene blocks and butadiene blocks.
Styrene blocks are responsible for thermoplastic properties, and butadiene blocks are responsible for flexural properties.
SBS has a high value in production, used in applications like low-level seals and grips, bitumen modification, footwear, and adhesives where chemical resistance and aging are not required.
When SBS is mixed with hydrogen, it becomes SEBS, eliminating the C=C bond in the butadiene component.
As a result, the SEBS grade has improved performance, heat resistance, mechanical properties, and chemical resistance.
Thermoplastic polyurethanes
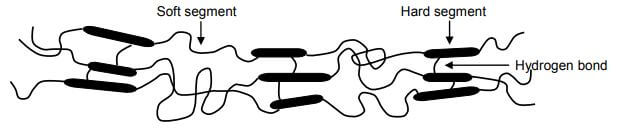
Source: Thermoplastic Elastomers, Edited by Prof. Adel El-Sonbati
These materials are based on polyester or polyether urethane types. They are used in applications needing flawless wear and tear resistance. Prime examples are industrial belting, footwear, wires, cables, etc.
Melt processable rubber (MPR)
MPR is designed for particular applications that require high-end chemical resistance. As a result, MPR is often replaced with nitrile rubber.
It has identical properties to vulcanized rubber in noise-dampening applications and has similar stress relaxation properties.
Primary applications include handgrips and weather grips for automobiles, coated fabrics and sheet goods, and window and door weatherstripping. These applications demand an excellent bond with thermoplastics like ABS and polycarbonate; MPR does it perfectly.
Due to high compression set values, MPR lags behind its peers in market share in the high-performance sealing market.
Thermoplastic polyether block amides
These polymers are known for their excellent chemical resistance and strong bonding with polyamide engineering plastics. The main applications are aerospace components, and wires, & cables.
Bio-based Thermoplastic Elastomers
Bio-based TPE polymer types have been developed to combat the dependence on non-renewable resources such as petroleum. Bio-based materials are the need of the hour.
These elastomers are made from biomass monomers derived from natural sources like corn, wheat, vegetable oils, starch, castor, canola oil, corn, soybean oil, etc.
Below are the most popular bio-based TPE plastic grades:
| Company | Grade name |
| ARLANXEO | Keltan® Eco – EPDM with bio-based material ranging from 50 to 70% |
| HEXPOL | Dryflex® Green – Renewable content of more than 90% |
| Avient | reSound™ OM grade – 30 to 50% bio-renewable content |
| FKuR | Terraprene® TPE – upto 90 bio-based content |
| DSM | Arnitel® ECO L700 & Arnitel® ECO M700 – 22 renewable content |
Applications
TPE plastic is considered for a job when flexibility is a top priority. It proves to be more beneficial than thermoset rubbers and traditional thermoplastics, with reduced costs, consistent production of higher quality products, and better safety while delivering on-par performance.
Let’s go through with application details:
| Industry | Applications | Reason |
| Automotive | Exterior & interior parts, bumpers, weather seals, shock dust boots, air ducts, pipe grommets, exterior & interior trims, instrument panels, drive belts, pressure pipes, mats, glass encapsulation, etc. | Excellent wear & abrasion resistance |
| Consumer Goods | Remote control covers, mobile phone covers, electronics protection covers, magnetic seals for appliances, push-button panels, etc | High flexibility and moldability |
| Electronics | Specialty cables, plugs & sockets, mobile phone components, Sheaths for condensers, etc | Good electrical properties and moldability |
| Medical & Healthcare | Seals, valves, breathing tubes, syringe seals, ventilation masks and bags, etc | Excellent chemical resistance, flexibility, and lightweight |
| Industrial | Seals, drums, suspension bushes, shock absorbers, roof membranes, inlet pipes, anti-vibration mounts, etc. | High Flexibility and chemical resistance |
| Footwear | Flippers, masks, ski-pole handles, ski boots, shoe soles, snorkels, etc | Abrasion resistance and flexibility |
Processability: TPE Material
TPE polymer can be processed seamlessly in traditional machinery like injection molding, extrusion, thermoforming, blow molding, calendering, and new-age 3D printing.
As mentioned at the beginning of the post, TPE material needs little or no compounding, the addition of reinforcing agents, stabilizers, or cure systems.
Injection Molding
Injection molding, without any doubt, is the most popular method for TPE processing, thanks to its high productivity rates and less waste generation.
The most common applications include finished parts, tubes, foams, etc. The processing capability of TPE is fine, and it sits in the hot runner without creating any problems.
- Mold Temperature – 25-50°C
- Melt temperature – 160-200°C
- Compression ratio: 2:1 to 3:1
- Screw ratio L/D: 20-24
All the numbers are ideal recommendations from our side. You can modify them depending on your needs.
Extrusion
The use of single screw extruders is highly recommended, equipped with three-section or barrier screws. The extrusion method is used for manufacturing foams and tubes.
- Melt temperature: 180-190°C
- L/D ratio of 24
- The compression ratio of 2.5:1 to 3.5:1
3D Printing
TPE polymer is compatible with 3D printing methods like FDM and SLS. The technique is utilized to produce flexible parts with complex geometries.
The most popular applications include phone covers, belts, springs, stoppers, etc.
The Difference Between TPE and TPV
| TPE | TPV |
| A material made by blending thermoplastic rubber and other auxiliary materials | TPV is a stable elastomer made by mixing EPDM + dynamically vulcanized PP. |
| Non-toxic, environmentally friendly, doesn’t contain carcinogenic substances, and can be recycled to achieve food sanitation standards. | Non-toxic, environmentally friendly, doesn’t contain nitrite and heavy metals, and can be recycled to achieve sanitation standards for coping with SGS certification and EU ROHS norms. |
| Slight changes in hardness can be seen in varied temperatures, ideal temperature range of – -30 ºC ~ 80ºC. | Slight changes in hardness can be seen in varied temperatures, ideal temperature range of – -30 ºC ~ 120ºC. |
| The Shore hardness is 4A in the same temperature range. | The Shore hardness is 5A in the temperature range of -20 ºC ~ 40ºC, which is much better than PVC and EPDM materials. |
| Good aging resistance | Good aging resistance |
| High Tearing strength | Good weathering resistance |
FAQs
Does TPE material need drying?
TPE material doesn’t necessarily need drying. However, if needed, it can be stored in a cool and dry environment for up to two years if maintained well in its original packaging and sealed well against moisture, heat, and other impurities.
Is TPE safe for Kids?
TPE is absolutely safe for kids as it contains a meager amount of extractable compounds that migrate from the surface of an infant care product. That’s a significant factor, assuming they put whatever babies touch in their mouths.
Is TPE better than PVC?
Both TPE and PVC have their pros and cons. They are known for their excellent flexibility and high strength making them suitable for various applications; however, one factor at which TPE fares better is its resistance to different chemicals such as oils and greases. Diluted acids and diluted alkalis.
Is TPE better than Latex?
It completely depends on the application for which it is being used. An example of bands made from latex is much more durable than those made from TPE or the combination of TPE and latex; however, as TPE has embedded properties of plastics, its fares significantly in terms of other mechanical and physical properties and also has substantially more applications.
Is TPE an FDA-approved material?
There are specific TPE grades that are FDA compliant. For example, Elastocon 2850PE and 2865PE grades of thermoplastic elastomers with Shore A hardnesses of 50 and 65 are FDA compliant and odorless.
Suggested Read –
- What is UHMW Plastic Material? | The Definitive Guide
- When Was Plastic Invented? | The History of Plastics
- What is HDPE Material?
- How is Plastic Made? A Simple and Detailed Explanation.
- What is Polyethylene? | How is Polyethylene Made | Types of Polyethylene | Processing of PE
Final Thoughts
In conclusion, TPE (Thermoplastic Elastomers) materials stand as a versatile class of polymers, merging rubber’s functional properties with thermoplastics’ processing advantages.
Their unique traits, like recyclability and adaptability to various manufacturing techniques, make TPEs valuable in numerous industries.
As a testament to sustainable innovation, TPEs present the potential for enhanced applications and performance in the future.
Thus, were my thoughts on TPE material. I hope you will find this post helpful. Kindly comment on your reviews in the comment box.
Keep Reading!
Quick Navigation


Good article. Do you know what kind of TPE is used for sexdolls? Where can I buy that kind in 1000 pound quantities? Where can I buy dyes for it? I’m designing some sexdolls of builds not available yet, female bodybuilder, and pretty bbw.
I was wondering the same about sex toys. Is TPE safe for inserting into the human body? Does it cause any irritation or poisoning? Are there any other concerns?
I replied to a comment but I don’t see the reply. I was wondering how safe TPE is when used to manufacture adult sex toys that are inserted into the human body. Any ideas?
Do TPE materials contain Black Rubber Mix chemicals: -N-Cyclohexyl-N-phenyl-4-phenylenediamine (CPPD); -N,N’-Diphenyl-p-phenylenediamine (DPPD); or -N-Isopropyl-N-phenyl-4-phenylenediamine (IPPD)?
TPE materials typically do not contain CPPD, DPPD, or IPPD, which are specific to black rubber mixes.
What kind glues are availble and effect to repair TPE products?
Use silicone adhesive or cyanoacrylate (super glue) for effective TPE product repairs.