Hello people, I have extensively researched a plastic material known as UHMW, known for its rigidness. Without further ado, let’s begin.
What is UHMW Plastic Material?
UHMW, short for ultra-high molecular weight polyethylene, is a tough and rigid plastic material known for its high abrasion and wear resistance. It is often also named high-modulus polyethylene (HMPE); it’s a subgroup of thermoplastic polyethylene with a more extended structure of chains, which helps transfer the weight and load to the polymer backbone more efficiently by reinforcing intermolecular linkages.
UHMW is adaptable to many industrial applications thanks to its durability, lightweight, chemical resistance, low friction, and one of the highest recorded impact strengths in any thermoplastic material—the molecular weight of the thermoplastic ranges from 3.1 million to 100 million grams per mole. As a result, it won’t be easy to melt it, making it perfect for high-temp scenarios.
Its properties and attributes are quite similar to HDPE, with the additional peculiarity of resistance to concentrated acids and alkalis, corrosive chemicals except for oxidizing acids, and organic solvents. Low moisture absorption, a low coefficient ( lower than Nylon and Acetal) to friction, low energy consumption, low maintenance, and self-lubrication are other quirks making UHMW stand out from many thermoplastics.
How is UHMW Made?

Like most plastics, polyethylene (the base monomer of UHMW) is created by distilling hydrocarbon fuels into lighter groups known as “fractions.” Some of the extracted fractions are combined with serval catalysts to produce plastics. Most thermoplastics will utilize the process of polymerization or polycondensation to produce commercial plastics.
UHMW is consolidated from its monomer ethylene, which is connected to create the base polyethylene byproduct. These molecules are magnitudes longer than the traditionally known HDPE because they are synthesized based on metallocene catalysts.
That type of synthesis results in UHMW molecules containing 100,000 to 250,000 monomer units per molecule compared to HDPE’s 700 to 1,800 monomers.
As mentioned earlier, it is a subgroup of polyethylene, consisting of long chains of polyethylene aligning in the same direction. The length of each molecular chain determines its strength. The distance-dependent interaction between the molecule is weaker for each atom of imbricate between the molecules.
However, as the molecules are extremely long, significant overlaps become more prevalent, adding to the capability of handling shear forces from molecule to molecule.
Each chain is bonded with others in distance-dependent interactions, making the overall intermolecular strength elevated. Talking particularly polymer chains can achieve a parallel orientation of more than 95% and a level of crystallinity from 39% to 75%.
Engaging Read – What is Bakelite: The Plastic That Changed the World
Key Properties of UHMW Material
- Compared to other high-strength materials, it has poor heat resistance because of the weak bonding between olefin molecules, which deranges the crystalline order of a given chain.
- Its melting point is about 155°C and it turns brittle at temperatures below −150 °C. So, long-term exposure to a cold temperature is not advisable.
- It does not readily absorb water or become wet because olefins lack polar groups, making any polymer readily bond with water.
- Specific Grades of UHMV are FDA compliant for visible x-ray vision technology. Excellent wear and impact resistance and low sliding properties make it more suitable for such applications.
- The simple molecular structure gives an edge to UHMW in terms of surface and chemical properties rarely seen in high-performance polymers.
- It is resistant to water, moisture, UV radiation, chemicals, and micro-organisms, but specific aggressive agents can quickly attack it.
- Under tensile stress, it will misshape or deform continually for the time the stress is present.
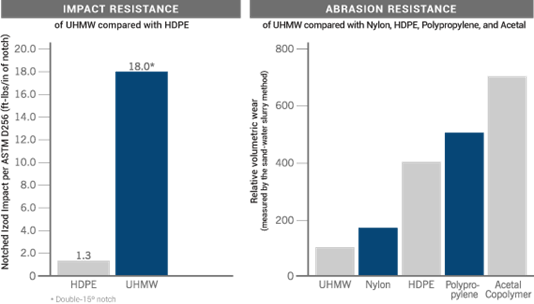
Source - curbellplastics.com
Here is a table with all the specific properties of UHMW:
[su_table responsive=”yes”]
| Property | Unit |
| Tensile Strength | 3100 psi |
| Specific Gravity | 1.45 g/cc |
| Hardness, Shore D | 64 |
| Flexural Modulus | 61-110 ksi |
| Compressive Strength | 3600 psi |
| Water Absorption @ 24H/Saturation | 0.01% |
| Izod Impact, Notched | 18 ft-lbs/in. |
| Compressive Modulus | 84 ksi |
| Coefficient of Friction | 0.14 |
| Melting Point | 155°C |
| Maximum Service Temperature | 82-85°C |
| Elongation at Break | 125% |
[/su_table]
Disadvantages
Although there are a few, I will still go through the drawbacks of ultra-high molecular weight polyethylene.
- It has a low melting point of 155°C, which is relatively low compared to other high-performance polymers, making it unstable for high-temperature applications.
- Low-coefficient of friction can also become a drawback depending on the application.
- As mentioned earlier, under a constant load, it develops “creep,” meaning a moderate elongation of fibers.
Fascinating Read – Food Grade Plastic: The Best Plastics for Food Applications
Applications
- Industrial Applications
- Wires & Cables
- Manufacturing
- Medical
- Marine Infrastructure
1. Industrial Applications
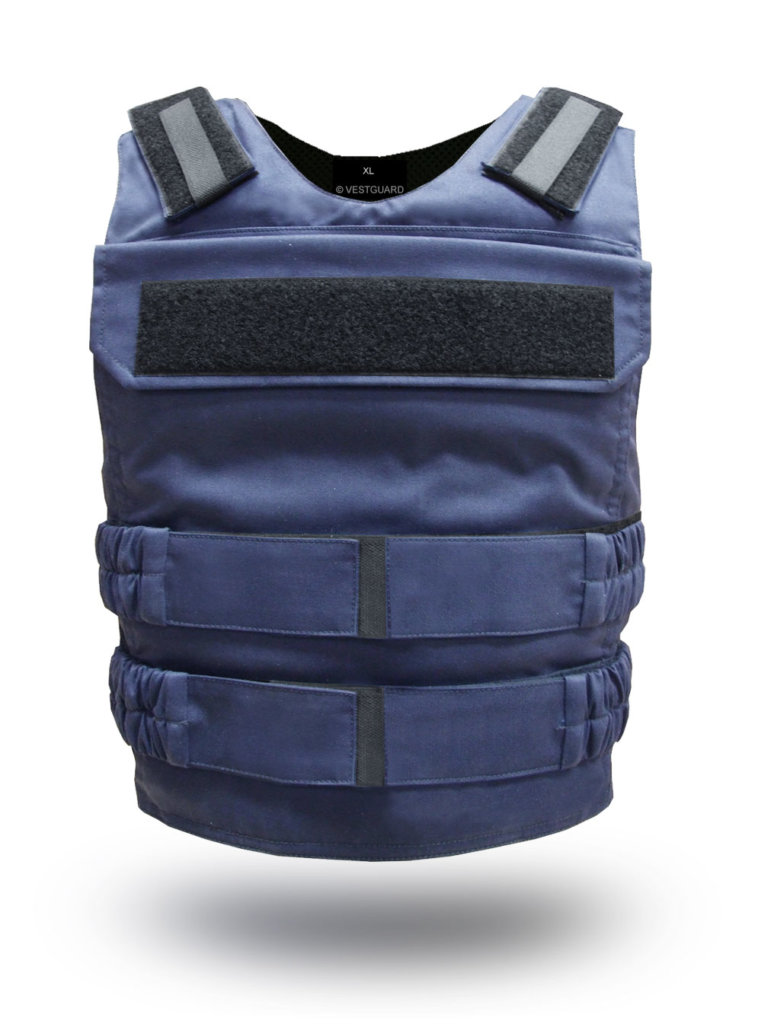

The brands like Dyneema and Spectra have developed UHMW with a high yield strength of 2.4 GPa (2.4 kN/mm2 or 350,000 psi), making it as strong as steel. The branded plastic material is used in vehicle and personal protection armors, bowstrings, automotive winching, climbing equipment, spear lines for spearguns, cut-resistant gloves, high-performance sails, suspension lines in parachutes, paragliders, etc.
Lower mass and lower elongation to breaking are crucial for UHMW being used in many industrial applications.
Talking about Dyneema and Spectra, ropes used in parachutes have almost no snap-back, don’t create kinks causing weak spots, and being a rope instead of a cable unravels sections that may appear at the length of the rope cannot penetrate the body like wire can.
UHMW plastic has the edge over the traditional monofilament line as it stretches less, has a thinner structure, and is more abrasion-resistant.
2. Wires & Cables
UHMW fluoropolymer insulation protection cables are extremely popular in the wires & cables industry. It contains some ECTFE and is chemically resistant to chlorine, sulfuric acid, and hydrochloric acid. The UHMW jacketing on the cable provides excellent mechanical and pliable strength during installation and operations.
3. Manufacturing
Ultra-high molecular weight polyethylene is heavily utilized in manufacturing PVC windows and doors because of the heat-withstanding capability of PVC-based materials. It is also used in various PVC shape profiles to be “bent” or shared around a template.
4. Medical
UHMW has a long history of aligning with medical science as a biomaterial for knee, hip, and spine replacement implants. The high-performance polymer was first introduced to medical science in 1962 by Sir John Charnley and became a prominent force as a material for hip and knee replacement in the 1970s.
The initial attempt was highly unsuccessful, but some early success was seen in the 1990s after the improvement in the development of highly cross-linked UHMW.
Today highly cross-linked UHMW material has become mainstream in clinical hip replacement, at least in developed countries. A trend has been picking pace in the past decade: using fibers for sutures. The sutures are flatter than conventionally used sutures made from polyester and poly-blends, making their application in the medical industry easier.
5. Marine Infrastructure
UHMW is used for manufacturing the mooring of ships and floating structures. The UHMW forms good contact between the floating structure and the field one. The features such as wear resistance, which is better than steel, impact resistance, similar to steel, and self-lubrication, make it ideal for applications in facing berthing structures.
History and Development of UHMW Plastics
Ultra-high molecular weight polyethylene was commercialized in the 1950s by Ruhrchemie AG. Today UHMW powder material is manufactured by serval manufacturers such as Mitsui, DSM, Ticona, Teijin, Celanese, and Braskem. Now, it is widely available in fibers, sheets, and rods.
Future Trends For UHMW Material
Global Ultra High Molecular Weight Polyethylene Market Share, by End-Use Industry, 2018 (%)
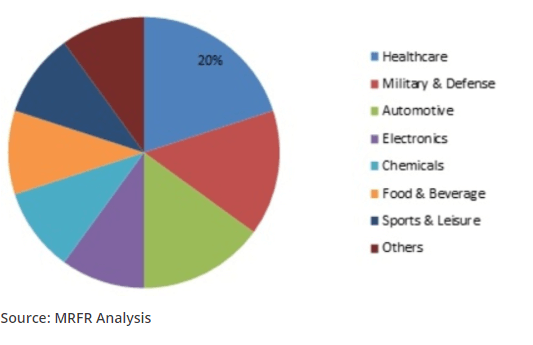
According to research conducted by Market Research Future, the estimated market size of Ultra-high molecular weight polyethylene was projected to be USD 1.8 Billion. It will register a 9.5 CAGR to reach USD 3.4 Billion by the year 2024. The growth is mainly driven by robust demand for UHMW-made orthopedics implants in Europe and North America.
It is also being used for making non-absorbable sutures as they’re tough and durable. Additionally, the demand will jump due to its exposure to the military and defense industry demanding personal protective equipment and anti-ballistic applications.
FAQs
What is the difference between UHMW and HDPE?
Both materials have very similar properties, but there is a difference in their respective applications. HDPE is easy to shape and weld using any thermoplastic equipment, making it ideal for applications with a specific shape. Conversely, UHMW is compatible with holding up against wear from constant friction with moving parts. It can also be fabricated and machined but is unsuitable for forming specific shapes.
How do you cut UHMW plastic?
Using a coarse blade is the option to cut the UHMW sheet. Another option is a carbide blade which cuts well. Using Teflon spray on the blades’ sides for cutting makes the process smoother.
Is UHMW the same as Teflon?
No. UHMW is a subset of polyethylene, and Teflon is a brand name for a synthetic chemical called polytetrafluoroethylene (PTFE).
Can UHMW be welded?
Yes. UHMW is very much weldable. I recommend using Virgin material for welding but regrind will also work fine. You might have difficulty welding some colors because of some pigments and dyes used.
How do heat and bend UHMW?
The thermoplastic has a low melting point of 155°C. And for bending, you can use rudimentary tools to accomplish desired shapes.
Suggested Read
- 7 Types of Plastics | An Helpful Illustrated Guide
- 6 Best Plastic Molding Techniques | A Complete Analysis
- What is PETG Material? | The Definitive Guide
- What is PET Plastic | PET Characteristics | PET Copolymers | How are PET Made | Advantages & Disadvantages
- What is 3D Printing? | Types of 3D Printing | Applications of 3D Printing | Advantages & Disadvantages
- What is Expanded Polystyrene (EPS) Foam? | EPS Manufacturing Process | EPS Properties | Expanded Polystyrene Vs. Extruded Polystyrene | Advantages and Disadvantages
- What is Processing and Drying Temperatures of Plastics
- What is TPE Material? | The Definitive Guide
Final Thoughts
That was my take on UHMW material and all its attributes. Ultra High Molecular Weight is a game-changer in the polymer industry, offering exceptional wear resistance, low friction, and impressive impact strength. As enterprises continue to seek innovative solutions for demanding applications, UHMW’s versatility and durability make it a prime candidate for widespread adoption.
Embracing UHMW material will undoubtedly lead to increased efficiency, longer-lasting components, and a more sustainable future across various sectors.
We appreciate your engagement and would love your thoughts and insights on this topic. Please share your opinions, experiences, or questions in the comment section below.
We value your input and hope to foster meaningful dialogue. We are wishing you a fantastic day ahead!
Quick Navigation

