Hello, Wonderful people. I hope you’re doing well. Today I’m going to share a fascinating piece on HDPE Melting Point, Repeat Unit, Properties, Advantages & Disadvantages.
HDPE has a melting point that falls within the range of approximately 120°C to 180°C (248°F to 356°F), with an average melting point of approximately 130°C (266°F).
Nevertheless, it is crucial to consider that the melting point of HDPE can differ based on the material’s grade and quality.
For example, HDPE materials of superior quality with higher degrees of crystallinity will have higher melting points than those of inferior quality with lower degrees of crystallinity.
The temperature at which a solid substance transitions from a solid to a liquid state is known as its melting point. In the case of HDPE, its melting point is influenced by its degree of crystallinity.
HDPE is categorized as a semi-crystalline polymer due to its combination of crystalline and amorphous regions.
Factors such as cooling rates, processing temperature, and molecular weight can affect the degree of crystallinity, leading to variations in the melting point.
This article offers an extensive evaluation of the melting point of HDPE and its influence on its general properties, along with other essential aspects.
Before diving into the subject, it’s crucial to define the term “melting point.”
Definition of Melting Point and How It is Measured?
The melting point of plastic refers to the specific temperature at which the plastic changes from a solid state to a liquid state.
This characteristic is vital because it dictates the suitable temperature range for processing the plastic material, applicable to procedures such as extrusion, injection molding, and various other thermal processes.
The most prevalent technique for determining the melting point of plastic materials is Differential Scanning Calorimetry (DSC).
DSC tracks the heat flow involved with the polymer during heating or cooling at a regulated pace.
By examining the endothermic peak on the heat flow chart, which represents the energy necessary for the polymer to melt, the melting point is identified.
Another method of determining the melting point involves using hot-stage microscopy, which allows for the direct observation of the polymer’s melting progression.
How HDPE Melt Temp Affects its Other Properties
Mechanical Properties
From a mechanical properties perspective, the melting point is integral to HDPE’s tensile strength and rigidity.
As the temperature approaches the melting point, the material’s mechanical properties, such as its tensile strength and hardness, decrease.
When HDPE is solid (below its melting point), the polymer chains are closely packed together, leading to the material’s renowned high tensile strength.
However, once the temperature exceeds the melting point, the HDPE starts to soften, and the polymer chains can slide past each other more efficiently, reducing HDPE density and stiffness.
Physical Properties
The melting point profoundly affects HDPE’s physical properties. When temperatures are below its melting point, HDPE maintains a solid, opaque state and exhibits high chemical resistance.
The material’s strong resistance to chemicals can be attributed to its high crystallinity, which is influenced by its melting point.
The crystalline zones in HDPE are closely packed and well-ordered, presenting a substantial barrier to chemical intrusion.
Yet, this orderly crystalline framework disintegrates when the temperature approaches the melting point, potentially undermining HDPE’s ability to resist chemicals.
Thermal Properties
The thermal properties of HDPE are similarly influenced by its melting point. The material exhibits good thermal stability and can withstand temperatures up to its melting point without significant degradation.
HDPE also has a relatively low coefficient of thermal expansion, meaning it doesn’t expand or contract significantly with changes in temperature until its melting point.
However, once the temperature rises above the melting point, HDPE begins to lose its thermal stability, which can lead to warping or melting.
Name and Identification of the Polymer
| Polymer Class |
High-Density Polyethylene
|
| Common Names |
HiTec, Playboard, Paxon, King Colorboard, Densetec, Polystone, King PlastiBal, and Plexar.
|
| Acronym | HDPE |
| CAS # | 9002-88-4 |
| Repeat Unit | 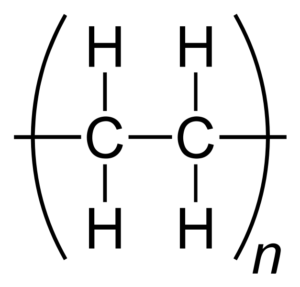 |
| CurlySmiles | C{-}C{n+} |
| Structure | 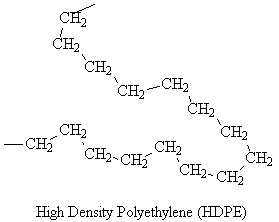 |
Thermo-Physical Properties
| Property | Value |
| Melting Point | 130 °C (266°F) |
| Density | 0.960 g mL-1 |
| Heat Deflection Temperature, 0.5 MPa | 72 °C |
| Heat Deflection Temperature, 1.8 MPa | 77 °C |
| Coefficient of Thermal Expansion x 10-5 | 14 cm °C |
| Thermal Conductivity | 0.42 W/ mk |
| Shore Hardness, D Scale | 55-67 |
Mechanical Properties
| Property | Value |
| Tensile Strength, Break at 23 C | 32 MPa |
| Tensile Strength, Yield at 23 C | 26 MPa |
| Elongation, Break | 600-1300% |
| Elongation, Yield | 10-18% |
| Tensile Modulus at 23 C | 900-1500 MPa |
| Flexural Modulus | 970-1250 MPa |
| Izod Notched |
71-155 J/m (kJ/m2)
|
| Izod Unnotched | No Break J/m |
Electrical Properties
| Property | Value |
| Dielectric Strength |
2.1-3.5 V/mm x 104
|
| Volume Resistivity |
6 x 1015 Ohm-cm
|
| Dielectric Constant @ 1 MHz | 2.2-2.4 |
| Dissipation Factor @ 1 MHz | 0.0001 – 0.0005 |
Fabulous Read – Polypropylene Melting Point, Properties and More
The melting point of HDPE is a critical factor to consider during its processing and manufacturing. When shaping or molding HDPE into the required form, the material is heated to a temperature higher than its melting point.
HDPE’s high melting point is a critical feature that guarantees the material’s shape and strength are preserved even in demanding circumstances.
In the construction sector, HDPE creates pipes and fittings that encounter high temperatures and pressure.
The high melting point of HDPE assures that these products can endure harsh conditions without experiencing degradation or melting.
Advantages
HDPE is a beneficial material with many salient advantages. Let us have a look at some of them:
- One of HDPE’s standout features is its malleability and moldability, which improves its applications substantially in the infrastructure industry. A good example is the underground piping sector, where HDPE is the most preferred plastic material thanks to its good weather ability and long-lastingness.
- HDPE has an outstanding strength-to-weight ratio of 0.93 to 0.97 g. That might not seem very impressive compared to LDPE. However, HDPE’s more linear structure with little branching gives it an edge over LDPE with greater tensile strength and greater molecular structure.
- It is corrosion-resistant, has good rigidity, and has a high melting point of 130 to 210°C. It’s difficult to melt, but its liquid form is easily processable to manufacture products like water tanks, shampoo bottles, cutting boards, detergent bottles, etc.
- It is easily recyclable and doesn’t lose its ability after being recycled. Recycled material is said to be as good as virgin material.
Disadvantages
- Non-resistant to chlorinated hydrocarbons.
- Non-resistant to oxidizing acids.
- High flammability
- High thermal expansion
FAQs
Below are the frequently asked questions on the melting point of HDPE. Let’s dig deep to know more.
Is HDPE safe to melt?
HDPE doesn’t get sticky once melted and can’t be easily removed once it cools down and while burning. If not added with any additives, it will burn clean and won’t release any toxic fumes. However, when you add pigments, antioxidants, antistats, and other lubricants, the outcome differs, and toxic fumes are released. So, in a nutshell, it’s fine to burn HDPE using general laboratory equipment.
What type of material is HDPE?
HDPE comes from a polyethylene family of thermoplastics and is produced from the monomer ethylene. Therefore, it is also sometimes referred to as “alkathene” or “polythene” when used for HDPE pipes.
Why HDPE melting point is higher than LDPE?
HDPE has a more linear and crystalline structure, and LDPE is softer and more flexible. Their fundamentally different internal composition results in differences in many physical attributes, and melting point is one of them.
Why is HDPE being used more in Hospitals?
HDPE is becoming very popular these days for healthcare and medical applications. Its salient features include high impact resistance, low moisture absorption, corrosion resistance, chemical resistance, and easy processing. Hospitals rely on HDPE to create cost-effective, dependable medical devices that don’t splinter, rot, or retain bacteria.
Can I recycle HDPE and LDPE together?
Unlike other plastics, HDPE and LDPE are miscible to be recycled together, but it is advisable to recycle them separately to keep their physical properties intact.
The Conclusion
That was all I had to say about HDPE melting point, properties, repeat unit, advantages & disadvantages.
To summarize, HDPE is a versatile and robust material that has various applications. Its melting point is a crucial property that plays a significant role in its processing and use.
The melting point of HDPE typically ranges from 120°C to 180°C (248°F to 356°F), with an average melting point of 130°C (266°F).
The degree of crystallinity is a factor that can influence the melting point, and careful temperature control during processing is necessary to prevent material degradation.
The high melting point of HDPE ensures that it can endure harsh conditions and maintain its strength and durability, making it an ideal material for use in diverse applications.
Thanks for bearing with my awful writing. Share your thoughts and questions in the comment box.
Have an outstanding day ahead.
Quick Navigation


Thanks for taking the time to collect the information and write this article. I’m not a chemist, I’m a tinkerer, but I understood what your wrote. Nicely done, Sagar.
Thanks for the compliment
It’s nice to find an article which gives me exactly the facts I’m looking for. Very technical and thorough. Well done. Thank you.
Thanks
I join the readers and I thank you for sharing your knowledge. It is useful.
Your very welcome