How is Polypropylene Made
Polypropylene is made from the polymerization of propylene gas by utilizing a Ziegler-Natta or metallocene catalyst. The polymerization variables are pressure, temperature, and reactant concentrations, which are decided according to the desired polymer grade.
Polypropylene is a semi-rigid and high-temperature resistant thermoplastic made from propylene monomers.
Its linear chemical structure makes it one of the best fatigue-resistant thermoplastics.
It boasts excellent electrical and chemical properties, thus used to create a wide range of products in various industries such as Agriculture, construction, and electronics.
There are various production methods used for making polypropylene. Still, they are essentially in a gas phase (fluidized bed or stirred reactor) or a liquid-phase process (slurry or solution).
Let’s talk about both processes.
Gas-Phase Process
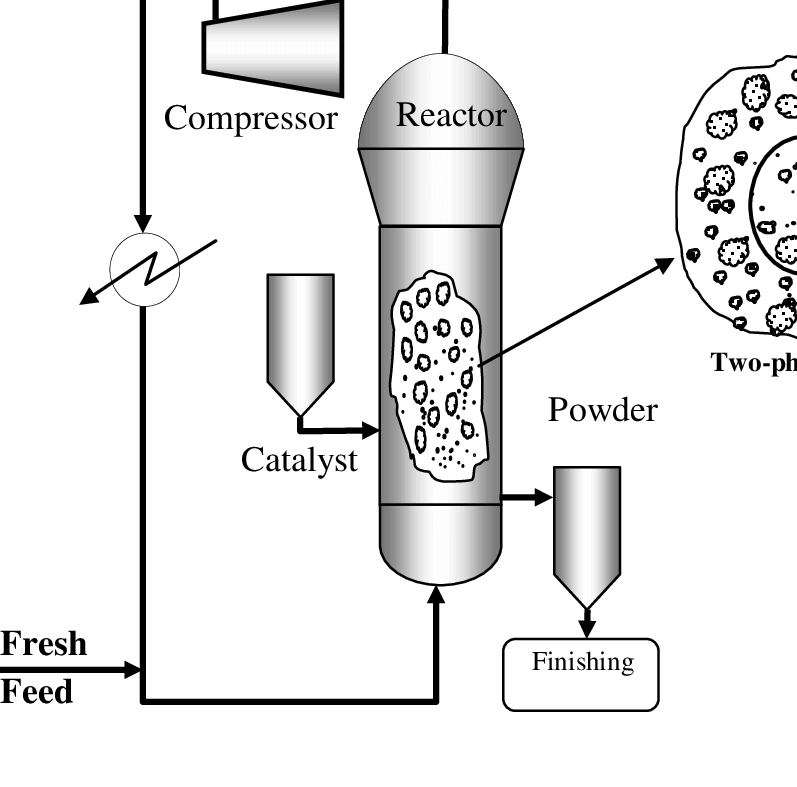
Here, the reaction takes place in a fluidized bed reactor at a temperature of 70°C to 100°C (158 °f to 212 °f) and a pressure of 1-20 atm.
The two gases which will play a vital role in this method are propane and hydrogen.
The gases will be transferred to a catalytic bed, and the propane will be converted into propene, which will later be converted into polypropylene in a fine powder form.
The polypropylene will be segregated from unreacted propene and hydrogen using cyclone separators. Furthermore, the fine powder is converted into pallet form for further usage.
The gas-phase process is inexpensive, flexible, and can make room for many catalysts, improving efficiency and eradicating gaseous and aqueous pollutants.
Liquid-Phase or Spheripol Process
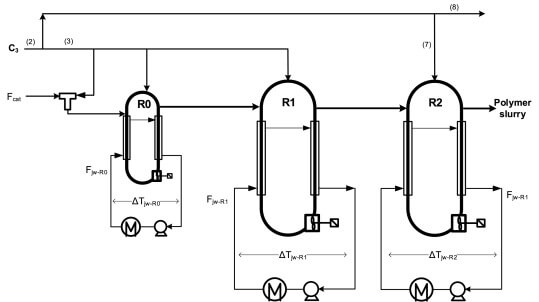
This method utilizes ethylene, propane, and hydrogen in polypropylene. The reaction occurs by blending the catalyst and monomer units in light hydrocarbons, an inert solvent that works best for this job.
The blend is poured into the vertically stirred gas phase reactors, where polymerization gets full swing.
After the polymerization, dip tubes extract the monomer and polymer powder blend from the reactors.
The polymer and carrier gas are separated by introducing nitrogen into the mixture in a purge vessel.
The polymer is then collected while the carrier gas and nitrogen are released. The resulting polymer is stored or transported for further use.
As what polypropylene is made of is out of the way, let’s look at the processing part of the polymer.
Interesting Read – How is Plastic made? A Simple and Detailed Explanation.
The Processing Of Polypropylene
Polypropylene, which is powdered, is transformed into pellets or chips through pelletizing. Common processing steps for polypropylene include.
- The polymer undergoes a filtration process to eliminate impurities and any remaining residues.
- These chips, which have a melt temperature suitable for injection molding between 473 K and 523 K, are extruded through the jets of a spinneret and extruder in a process known as Spinning.
- The newly extruded fibers are cut to the desired length and cooled by blowing cool air at a controlled speed of 3 𝑚3/𝑚𝑖𝑛 to prevent any damage to the fibers. This process is called Quenching.
- The internal stresses and tension in the fibers are relieved, and the density of the polymer in the fiber is increased through a process called thermosetting, which involves heating the fibers with hot air or steam.
The Conclusion
That was all I had to say about how polypropylene is made. I have also mentioned the processing of the infamous polymer to sweeten the deal. PP is a widely used polymer worldwide in various applications, so people working with polypropylene in some form or other will find this price very helpful.
Thanks, and have a lovely day.
Quick Navigation
